It’s All in the Applications
TNSR provides stellar packet per second and gigabit per second performance for the most demanding secure networking applications..

What is High-Throughput Site-to-Site IPsec?
The rise in worker mobility, distributed offices, and complex multi-cloud hosting of business applications is escalating organizations’ reliance on encryption. This puts computational strain on traditional VPN solutions, especially as bandwidth needs evolve from 1 to 10 to 40 Gbps or more. Traditional router/VPN appliances buckle under the load - particularly when the packet traffic shifts towards IMIX. Today's businesses need higher throughput site-to-site VPN solutions that can handle a variety of application-driven packet sizes - without breaking the bank. TNSR software shines at high-performance site-to-site IPsec, especially when compared to traditional solutions underpinned by kernel-based, single packet-at-a-time processing approaches.

Routed IPsec site-to-site
Internet Key Exchange
DH Groups
Message Auth. Code Algorithm
Encryption Algorithms
IPsec
VRRP
High-Throughput Site-to-Site IPsec VPN Features
Routed IPsec site-to-site
A site-to-site IPsec tunnel interconnects two networks as if they were directly connected by a router. Systems at Site A can reach servers or other systems at Site B, and vice versa. This traffic may also be regulated via firewall rules, as with any other network interface. If more than one client will be connecting to another site from the same controlled location, a site-to-site tunnel will likely be more efficient, not to mention more convenient and easier to support.
With a site-to-site tunnel, the systems on either network need not have any knowledge that a VPN exists. No client software is needed, and all of the tunnel work is handled by the tunnel endpoints.
More information can be found in our documentation.
Internet Key Exchange
Internet Key Exchange (IKE) is the protocol used to set up a secure, authenticated communications channel between two parties. IKE typically uses X. 509 PKI certificates for authentication and the Diffie–Hellman key exchange protocol to set up a shared session secret. TNSR supports both IKE-v1 (more widely supported) and IKE-v2 (more secure).
More information can be found in our documentation.
DH Groups
Diffie-Hellman (DH) groups determine the strength of the key used in the key exchange process. Higher group numbers are more secure, but require additional time to compute the key. TNSR supports DH Groups 1-24, and 31.
More information can be found in our documentation.
Message Authentication Code Algorithm
A Message Authentication Code (MAC) algorithm is an integrity algorithm - based on a symmetric key cryptographic technique - used to provide message integrity and authentication. TNSR supports aescmac, aesxcbc, md5, sha1, sha256, sha384 and sha512 message integrity algorithms.
More information can be found in our documentation.
Encryption Algorithms
Ciphers (algorithms) are used to encrypt and decrypt data as it traverses a VPN connection. Algorithms based on AES are common and secure, and are widely supported by VPN implementations. AES-GCM, or AES Galois/Counter Mode is an efficient and fast authenticated encryption algorithm, which means it provides data privacy as well as integrity validation, without the need for a separate integrity algorithm. Additionally, AES-based algorithms can often be accelerated by AES-NI.
TNSR supports a number of common, secure encryption algorithms including 3DES, AES-128-CBC, AES-192-CBC, AES-256-CBC, AES-ICV16-GCM-128, AES-ICV16-GCM-192, AES-ICV16-GCM-256, Camellia-128,Camellia-192, Camellia-256 and CHACHA20-POLY1305.
More information can be found in our documentation.
IPsec
IPsec is a group of protocols used together to set up encrypted connections between devices. It helps keep data sent over public networks secure. IPsec is often used to set up VPNs, where it both encrypts IP packets and authenticates the source from where the packets originated.
More information can be found in our documentation.
VRRP
The Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) enables hosts on a LAN to make use of redundant routing platforms on that LAN without requiring more than the static configuration of a single default route on the hosts. This increases the availability and reliability of routing paths via automatic default gateway selections - via an election protocol - on an IP subnetwork. The advantage of VRRP is high availability without requiring configuration of dynamic routing or router discovery protocols on every end-host.
More information can be found in our documentation.
Who Needs High-Throughput Site-to-Site IPsec VPN?

Businesses, Educational Institutions and Government Agencies
Any business, educational institution, or government agency looking for high-throughout encrypted connections - across campuses, from office to cloud, from data center to cloud, or between public or private Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) - but have been severely limited by traditional VPN solutions which significantly degrade network connection throughput, or come at an exorbitant price.

Service Providers
Any service provider looking for high-throughout encrypted connections - to address customers’ connectivity needs across campus, office to cloud, data center to cloud, or inter-Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) - at compelling price points.
Where Should IPsec Site-to-Site VPNs Be Deployed?
There are two types of site-to-site VPNs: Intranet-based and Extranet-based. Intranet-based site-to-site VPNs connect multiple geographically-disparate LANs into a single private network, i.e., a Wide Area Network. Extranet-based site-to-site VPNs enable a company to connect its LAN to LANs within one or more other companies so information can be securely shared between partners, as an example.
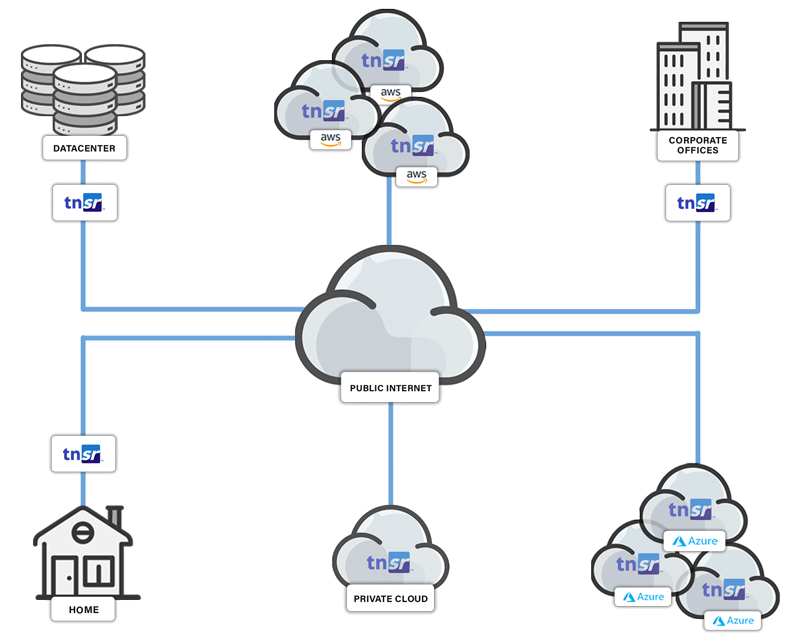
What Makes TNSR a Great Site-to-Site IPsec VPN Solution?
High Throughput
- Leverages Vector Packet Processing (VPP) to improve packet processing performance one to two orders of magnitude over kernel-based processing solutions
- Performance scales as connection bandwidth increases, and as packet sizes fall from jumbo frames to IMIX to pure 64 byte traffic - driven by the most demanding applications
Feature Rich
- Bridging, Static Routing, Dynamic Routing, BGP, OSPF, ECMP, BFD, VRF and more
- Integrates VPP, DPDK, FRR, strongSwan, Clixon, RESTCONF open source technologies and more into a turnkey, ready to use commercial product
Easily Scalable
- Scale out with appliances, virtual machines or cloud instances
- Scale up by increasing bandwidth per instance to the limit of hardware capabilities, no license constraints
- Leverage crypto offload for additional performance scale up
Excellent overall solution value
- Unbeatable packet processing price-performance for site-to-site VPN applications
- No feature, bandwidth or other incremental licensing charges
- Leverages the most advanced open source technologies
- Commercial subscriptions include the full benefit of seasoned global support specialists
-01.png?width=926&height=181&name=Netgate%20Logo%20PMS%20(horizontal)-01.png)
%201.png?width=302&name=Netgate%20Logo%20PMS%20(horizontal)%201.png)
